Generation 4 Servoregulator
In Process
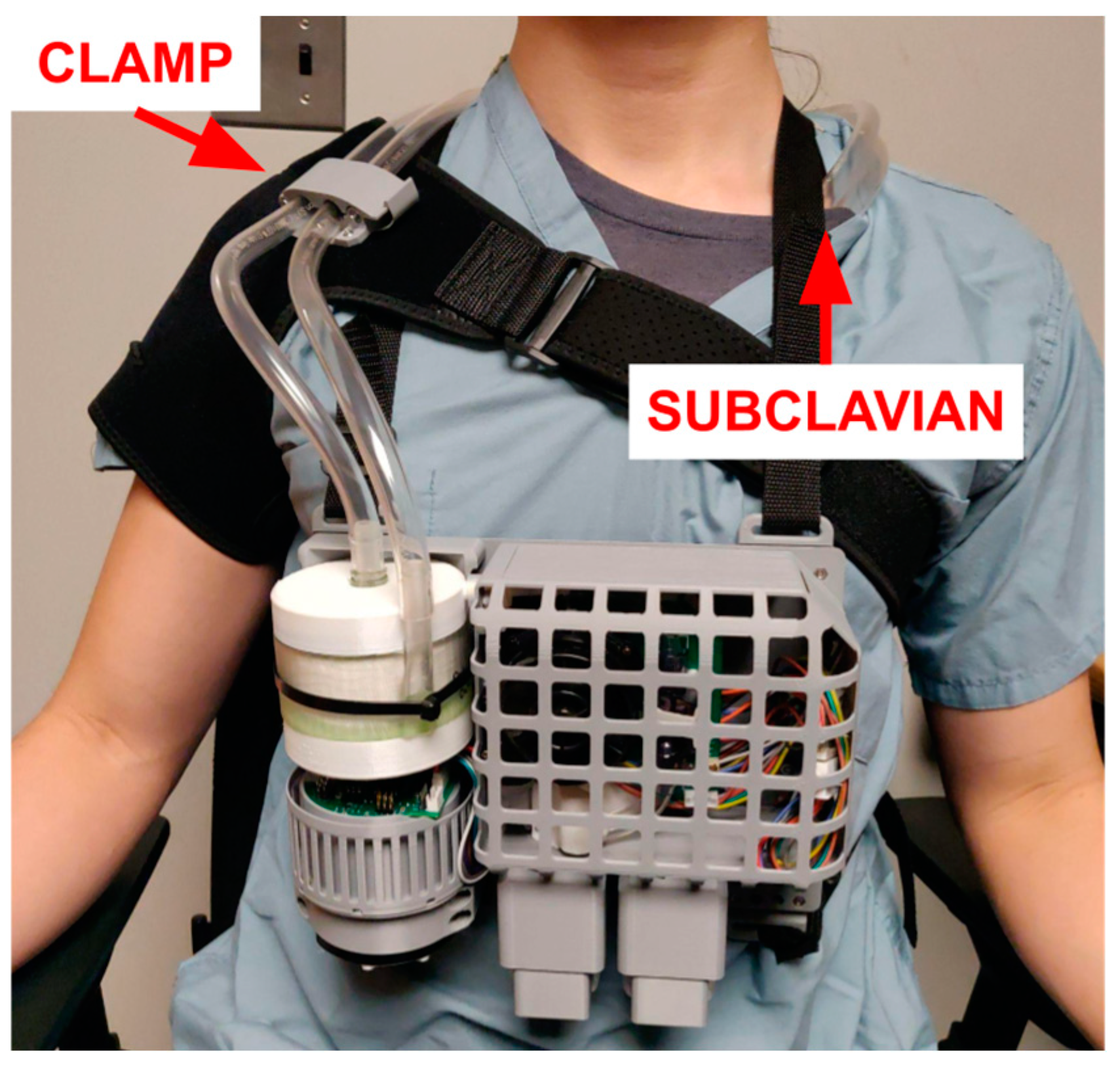
Wearable Servoregulator
Built “Wearable” ServoRegulator for CO2 removal. The new design is smaller and wearable, and is also more robust and integrated to bring it from a benchtop proof-of-concept to a portable minimum viable product.
Published Paper: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5354/11/10/969
Extracorporeal Carbon Dioxide Removal (ECCO2R) systems support patients with severe respiratory failure. Concurrent ambulation and physical therapy improve patient outcomes, but these procedures are limited by the complexity and size of the extracorporeal systems and rapid changes in patient metabolism and the acid–base balance. Here, we present the first prototype of a wearable ECCO2R system capable of adjusting to a patient’s changing metabolic needs. Exhaust gas CO2 (EGCO2) partial pressure is used as an analog for blood CO2 partial pressure (pCO2). Twin blowers modulate sweep gas through the AL to achieve a desired target EGCO2. The integrated system was tested in vitro for 24 h with water, under varying simulated metabolic conditions and target EGCO2 values, and in a single test with whole blood. When challenged with changing inlet water pCO2 levels in in vitro tests, the system adjusted the sweep gas to achieve target EGCO2 within 1 min. Control runs with a fixed sweep gas (without negative feedback) demonstrated higher EGCO2 levels when challenged with higher water flow rates. A single in vitro test with whole ovine blood confirmed functionality in blood. This is the first step toward wearable ECCO2R systems that automatically respond to changing metabolism. Such devices would facilitate physical therapy and grant greater autonomy to patients.
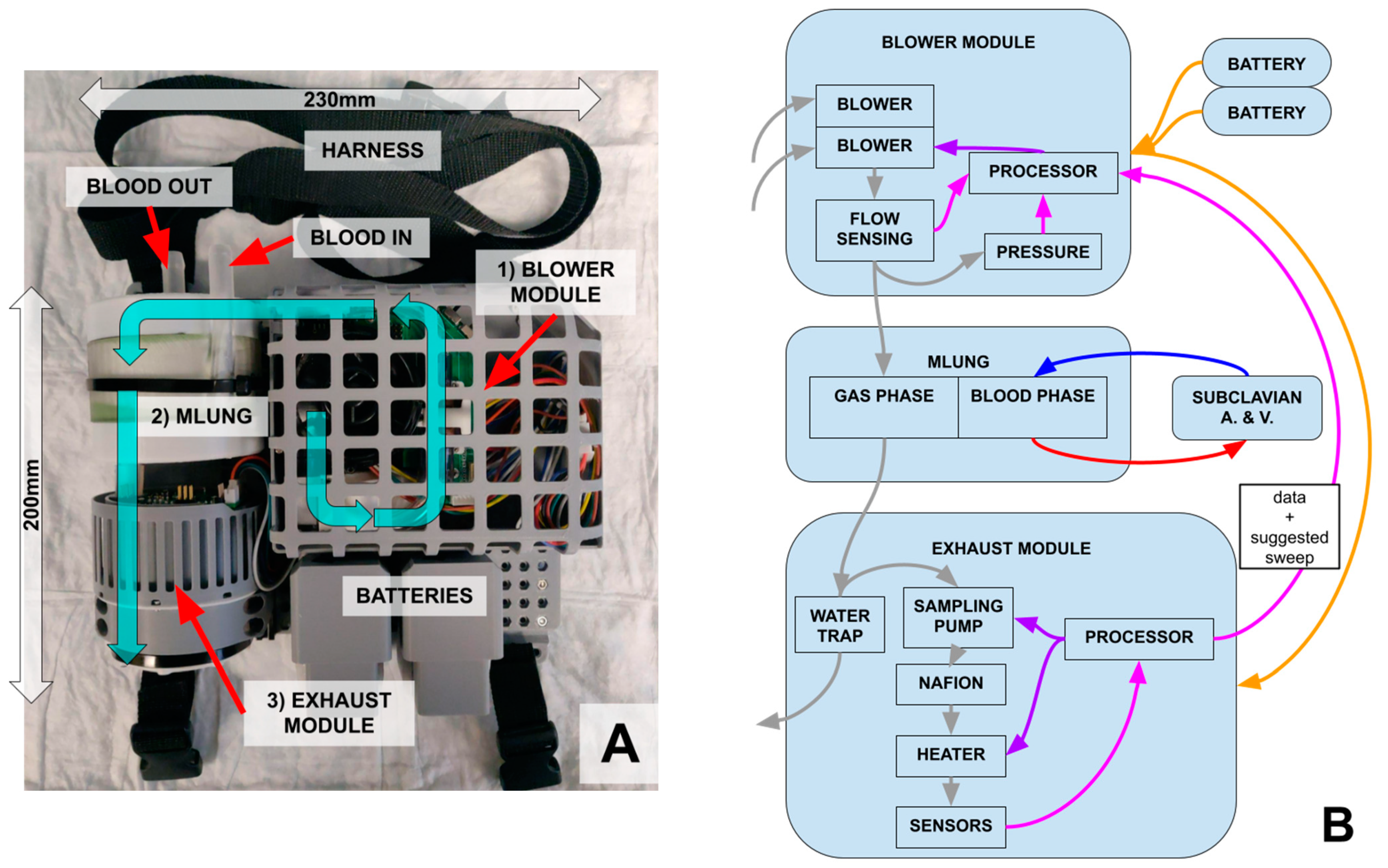
(A) Assembled and packaged prototype of the wearable ECCO2R system. Air (cyan arrows) is taken in from the blower module (1), pushed through the AL (2, MLung) where it removes CO2 from the blood, and then passes through the exhaust module (3), which reads the EGCO2. (B) Communication and control between system and subsystems. Gas flow is shown in gray, blood flow in red and blue, control in purple, power in orange, and data in pink.
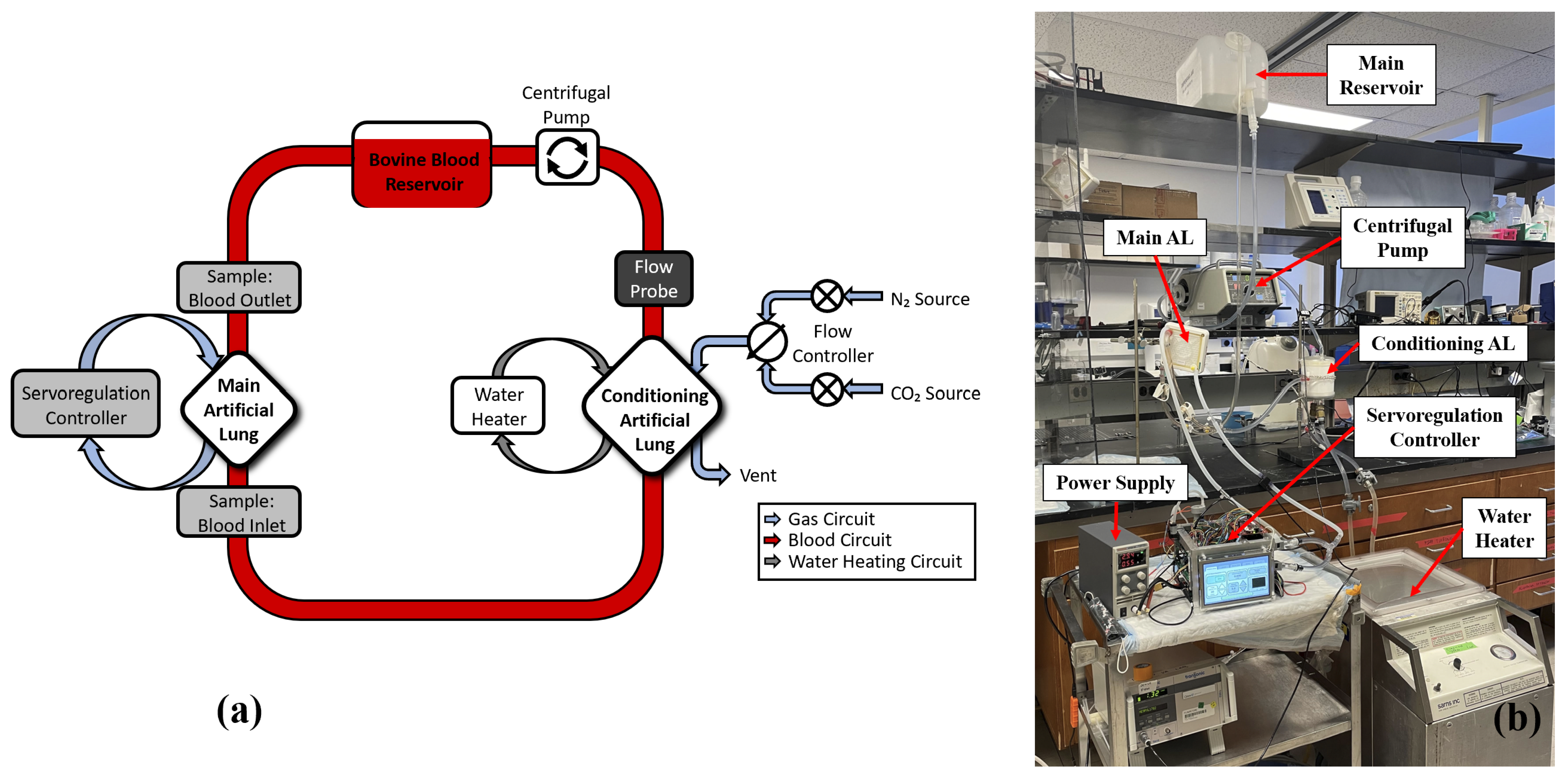
Generation 3 Servoregulator
Leading testing of a novel ServoRegulator which uses compressed N2, O2, and CO2, through blood and animal testing. The compressed gas allows it to be used for oxygenation (previous systems and the wearable system can remove CO2)
Published Abstract: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5354/9/10/593
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) systems aid patients with severe respiratory failure. However, current systems do not respond to changing patient metabolism and disease state, limiting patient comfort, activity, and rehabilitation. A system was developed that uses Exhaust Gas CO₂ (EGCO₂) partial pressure as an analog for blood CO₂ measurements. It modulates sweep gas flow rate through a membrane oxygenator in response to changing blood CO₂ levels to achieve a desired target EGCO₂ (tEGCO₂). This system was tested in vitro with bovine blood under varying blood flow rates, tEGCO₂ values, and simulated metabolic rates and compared to the current clinical standard of fixed sweep gas. An acute in vivo study was performed to validate functionality of the controller. When the system was challenged with changing blood CO₂ levels in in vitro and in vivo tests, it adjusted gas flow to meet the target EGCO₂ within 2 min. In the in vitro study, this resulted in a lower variation of post-oxygenator blood CO₂ compared with fixed gas flow.


Generation 2 ServoRegulator
- Built the enclosure for the previous (larger) ServoRegulator, and performed in-vivo animal testing.
Published Abstract: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5354/9/10/593